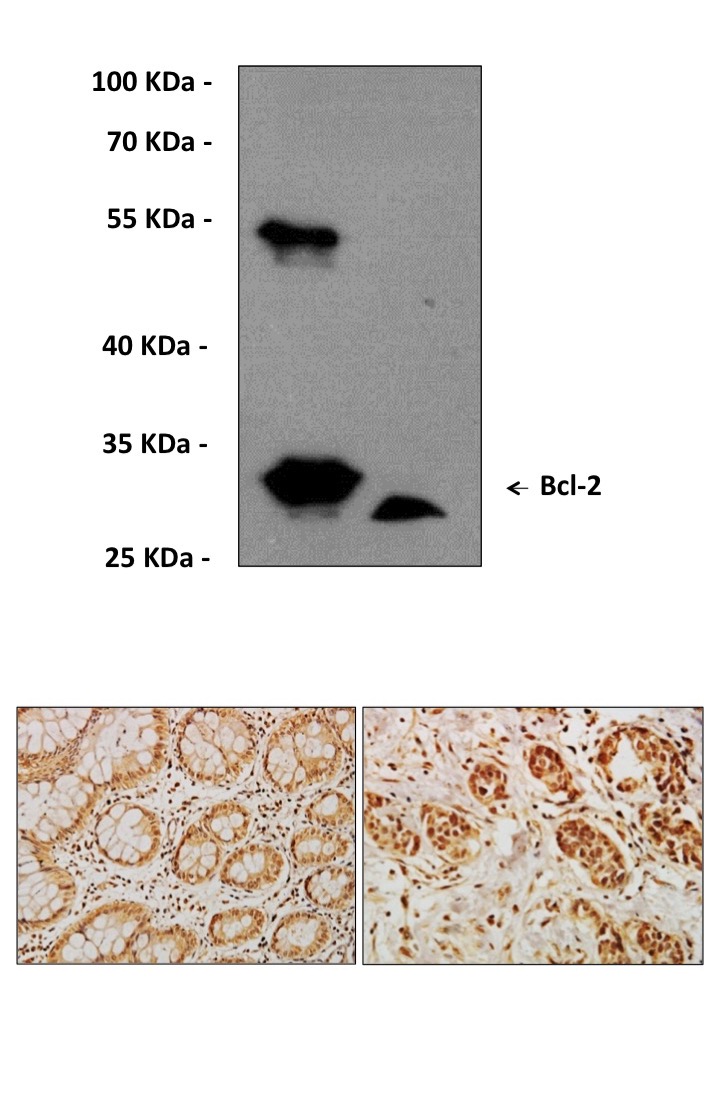
Anti-Bcl-2: Mouse Bcl-2 Antibody |
 |
BACKGROUND Bcl-2 exerts a survival function in response to a wide range of apoptotic stimuli through inhibition of mitochondrial cytochrome c release (1). It has been implicated in modulating mitochondrial calcium homeostasis and proton flux (2). Several phosphorylation sites have been identified within Bcl-2 including Thr56, Ser70, Thr74 and Ser87 (3). It has been suggested that these phosphorylation sites may be targets of the ASK1/MKK7/JNK1 pathway, and that phosphorylation of Bcl-2 may be a marker for mitotic events (4, 5). Mutation of Bcl-2 at Thr56 or Ser87 inhibits its anti-apoptotic activity during glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis of T lymphocytes (6). Interleukin 3 and JNK induced Bcl-2 phosphorylation at Ser70 may be required for its enhanced anti-apoptotic functions (7).
REFERENCES
1. Murphy, K.M. et al. (2000) Cell Death Differ.7, 102–111.
2. Zhu, L. et al. (1999) J. Biol. Chem.274, 33267–33273.
3. Maundrell, K. et al. (1997) J. Biol. Chem.272, 25238–25242.
4. Yamamoto, K. et al. (1999) Mol. Cell. Biol.19, 8469–8478.
5. Ling, Y.H. et al. (1998) J. Biol. Chem.273, 18984–18991.
6. Huang, S.J. and Cidlowski, J.A. (2002) FASEB J.16, 825–832.
7. Deng, X. et al. (2001) J. Biol. Chem.276, 23681–23688.
Products are for research use only. They are not intended for human, animal, or diagnostic applications.
Параметры
Cat.No.: | CC10036 |
Antigen: | Recombinant human Bcl-2 expressed in mammalian cells. |
Isotype: | Mouse IgG |
Species & predicted species cross- reactivity ( ): | Human, Mouse |
Applications & Suggested starting dilutions:* | WB 1:1000 IP n/d IHC 1:100 ICC 1:50 FACS n/d |
Predicted Molecular Weight of protein: | 26 kDa |
Specificity/Sensitivity: | Detects endogenous Bcl-2 proteins without cross-reactivity with other family members. |
Storage: | Store at -20°C, 4°C for frequent use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
*Optimal working dilutions must be determined by end user.
Информация представлена исключительно в ознакомительных целях и ни при каких условиях не является публичной офертой