Anti-Eg5: Mouse Eg5 Antibody |
 |
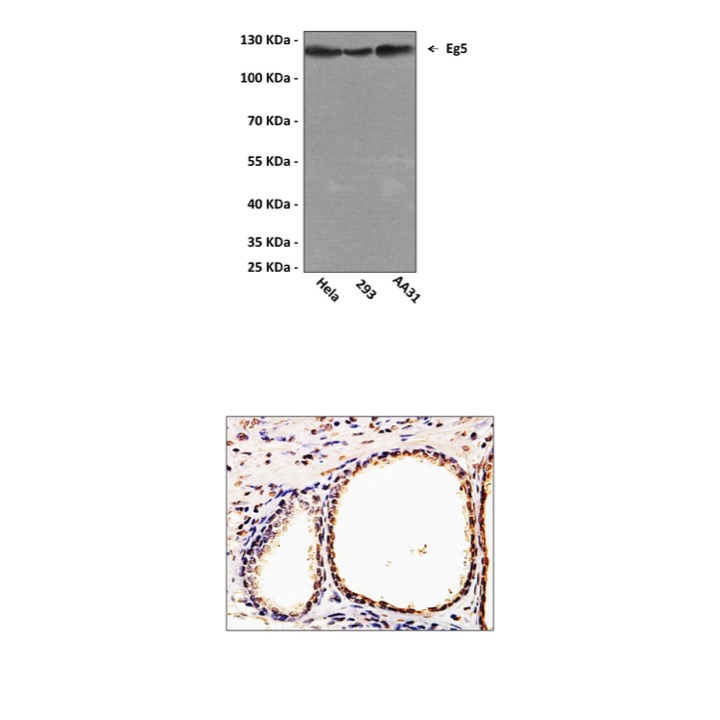
BACKGROUND Eg5 (also called kinesin-like protein 11 or Kif11) belongs to the kinesin-like family of motor proteins important in chromosome positioning, centrosome separation and mitotic spindle formation. Phosphorylation of Eg5 by mitotic kinases regulates its activity by modulating its association with microtubules (1, 2). Because anti-mitotic chemotherapeutic drugs, such as taxanes, target microtubules and have pleiotropic and sometimes toxic effects, drugs that target microtubule associated proteins such as Eg5 are currently in development (3-5).
REFERENCES
1. Blangy, A. et al. (1995) Cell 83, 1159-69.
2. Rapley, J. et al. (2008) J Cell Sci 121, 3912-21.
3. Sarli, V. and Giannis, A. (2006) ChemMedChem 1, 293-8.
4. Cox, C.D. et al. (2008) J Med Chem 51, 4239-52.
5. Nakai, R. et al. (2009) Cancer Res 69, 3901-9.
Products are for research use only. They are not intended for human, animal, or diagnostic applications.
Параметры
| Cat.No.: | CC10043 |
| Antigen: | Recombinant human Eg5 expressed in E. Coli |
| Isotype: | Mouse IgG |
Species & predicted species cross- reactivity ( ): | Human, Mouse |
Applications & Suggested starting dilutions:* | WB 1:1000 IP n/d IHC 1:100 ICC n/d FACS n/d |
Predicted Molecular Weight of protein: | 120 kDa |
| Specificity/Sensitivity: | Detects endogenous Eg5 proteins without cross-reactivity with family members. |
| Storage: | Store at -20°C, 4°C for frequent use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
*Optimal working dilutions must be determined by end user.
Информация представлена исключительно в ознакомительных целях и ни при каких условиях не является публичной офертой