Anti-FABP-4/AFABP: Mouse Fatty Acid-Binding Protein 4 Antibody |
 |
BACKGROUND Fatty acid-binding proteins (FABPs) are members of the superfamily of lipid-binding proteins (LBP). So far 9 different FABPs, with tissue-specific distribution, have been identified: L (liver), I (intestinal), H (muscle and heart), A (adipocyte), E (epidermal), Il (ileal), B (brain), M (myelin) and T (testis). The primary role of all the FABP family members is regulation of fatty acid uptake and intracellular transport. The structure of all FABPs is similar – the basic motif characterizing these proteins is beta-barrel, and a single ligand (e.g. a fatty acid, cholesterol, or retinoid) is bound in its internal water-filled cavity. Despite the wide variance in the protein sequence, the gene structure is identical. The FABP genes consist of 4 exons and 3 introns and a few of them are located in the same chromosomal region. For example, A-FABP, E-FABP and M-FABP create a gene cluster.1 Physiological roles of these proteins are not only involved in FA transport, but also in regulation of cell growth and differentiation, cellular signaling, gene transcription and cytoprotection.2 Because of their physiological properties some FABP genes were tested in order to identify mutations altering lipid metabolism and relating with other diseases.
FABP-4 is a fatty acid binding protein found in adipocytes. It binds both long chain fatty acids and retinoic acid and delivers long-chain fatty acids and retinoic acid to their cognate receptors in the nucleus. FABP4 delivers specific ligands from the cytosol to the nuclear receptor PPARγ in the nucleus, thereby facilitating the ligation and enhancing the transcriptional activity of the receptor.3 FABP-4 has been suggested to be a bridge between inflammation and other pathways related to the metabolic syndrome. In this regard, genetic variability at the FABP4 locus has been shown to be associated with plasma lipid levels, type 2 diabetes, and coronary heart disease risk.4
REFERENCES
1. Merkel, M. Et al: J. Biol. Chem. 277:7405-11, 2001
2. Hamilton, M.T. et al: Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 275: E1016-E1022, 1998
3. Kamei, Y. et al: Biochem. Int. 26:923-34, 1992
2. Hamilton, M.T. et al: Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 275: E1016-E1022, 1998
3. Kamei, Y. et al: Biochem. Int. 26:923-34, 1992
Products are for research use only. They are not intended for human, animal, or diagnostic applications.
Параметры
Cat.No.: | CP10096 |
Antigen: | Purified recombinant human FABP-4 fragments expressed in E. coli. |
Isotype: | Mouse IgG |
Species & predicted species cross- reactivity ( ): | Human, Mouse, Rat |
Applications & Suggested starting dilutions:* | WB 1:1000 IP n/d IHC n/d ICC n/d FACS n/d |
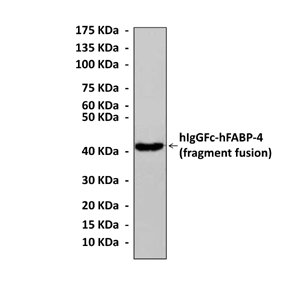
Predicted Molecular Weight of protein: | 14 kDa |
Specificity/Sensitivity: | Detects endogenous FABP-4 proteins without cross-reactivity with other family members. |
Storage: | Store at -20°C, 4°C for frequent use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
*Optimal working dilutions must be determined by end user.
Документы
Информация представлена исключительно в ознакомительных целях и ни при каких условиях не является публичной офертой