Anti-ADAMTS4: Rabbit A Disintegrin and Metalloproteinase with Thrombospondin Motifs 4 Antibody |
 |
BACKGROUND Members of the ADAMTS (A Disintegrin And Metalloproteinase with Thrombospondin Motifs) gene family are composed of at least 19 molecules and are involved in various biological and biochemical events such as fertilization, proteoglycan degradation, processing of fibrillar collagens, and intravascular coagulation.1 Members of the family share several distinct protein modules, including a propeptide region, a metalloproteinase domain, a disintegrin-like domain, and a thrombospondin type 1 (TS) motif. Individual members of this family differ in the number of C-terminal TS motifs, and some have unique C-terminal domains. Among them, ADAMTS1, ADAMTS4 (also referred to as aggrecanase-1 and hyalectanase), ADAMTS5 (aggrecanase-2), and ADAMTS9 cleave specific Glu–X bonds (where X is most often Ala or Gly) of the core protein of aggrecan, a major proteoglycan in articular cartilage. Studies suggested that the major aggrecan fragments found in vitro in response to cytokine-stimulated cartilage degradation and in vivo in arthritic joint fluids are generated through cleavage at Glu–X bonds by the glutamyl endopeptidase activity of these AD-AMTS members. Further studies demonstrated that ADAMTS4 is induced by stimulation of chondrocytes and synovial cells with interleukin-1, tumor necrosis factor-α, or transforming growth factor-beta, although ADAMTS5 is constitutively expressed.2 In addition, ADAMTS4 mRNA is found mainly in brain, lung, and heart. ADAMTS4 together with some other members of the ADAM protein family has been found to be upregulated consistently in breast carcinomas. ADAMTS4 is overexpressed by synovial cells and chondrocytes in osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Thus, ADAMTS4 is considered to play an important role in the aggrecan degradation of articular cartilage in osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Moreoever, the cleavage of aggrecan and brevican also suggests key roles of ADAMTS4 in the central nervous system, potentially, in the progression of glioma. The aggrecanase activity of ADAMTS4 is inhibited by TIMP-3 (tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-3) among the four TIMP proteins (TIMP-1–4), all of which were originally cloned as inhibitors of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs).3 As shown with ADAMTS1, ADAMTS4 has an affinity for extracellular matrix (ECM) molecules, being deposited in the ECM after synthesis. In fact, the binding activity of C-terminal CR and/or spacer domains of ADAMTS4 for sulfated glycosaminoglycans of aggrecan has been reported. Interestingly, the aggrecanase activity of full-length active ADAMTS4 is blocked probably through interaction with ECM molecules, and activity appears after removal of the C-terminal spacer domain. Thus, it is suggested that ADAMTS4 may have binding molecules by which the activity is regulated. Indeed, it was shown that fibronectin inhibits the aggrecanase activity of ADAMTS4 through the interaction between the C-terminal regions of each molecule.4 In fact, in vivo, production of proteolytically active ADAMTS4 require removal of the prodomain by a furin-like activity and also removal of a portion of the C-terminal spacer domain by other matrix metalloproteinases. It was reported that the MMP-17 cleaves and activates ADAMTS4 on the cell surface.5
REFERENCES
1. Llamazares, M. et al: J. Biol. Chem. 278:13382-8, 2003
2. Yamanishi, Y. et al: J. Immunol. 168:1405-12, 2002
3. Hashimoto, G. et al: FEBS Lett. 494:192-5, 2001
4. Hashimoto, G. et al: J. Biol. Chem. 279:32483-91, 2004
5. Gao, G. et al: J. Biol. Chem. 279:10042-51, 2004
2. Yamanishi, Y. et al: J. Immunol. 168:1405-12, 2002
3. Hashimoto, G. et al: FEBS Lett. 494:192-5, 2001
4. Hashimoto, G. et al: J. Biol. Chem. 279:32483-91, 2004
5. Gao, G. et al: J. Biol. Chem. 279:10042-51, 2004
Products are for research use only. They are not intended for human, animal, or diagnostic applications.
Параметры
Cat.No.: | CA1236 |
Antigen: | Short peptide from human ADAMTS4 sequence. |
Isotype: | Rabbit IgG |
Species & predicted species cross- reactivity ( ): | Human, Mouse, Rat |
Applications & Suggested starting dilutions:* | WB 1:1000 IP n/d IHC 1:50 - 1:200 ICC n/d FACS n/d |
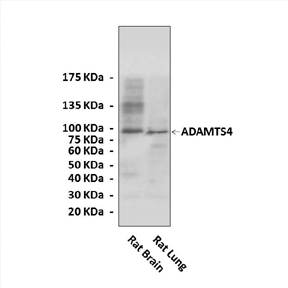
Predicted Molecular Weight of protein: | 90 kDa |
Specificity/Sensitivity: | Detects endogenous levels of ADAMTS4 proteins without cross-reactivity with other related proteins. |
Storage: | Store at -20°C, 4°C for frequent use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
*Optimal working dilutions must be determined by end user.
Документы
|
| ||||||||||
| ||||||||||
Информация представлена исключительно в ознакомительных целях и ни при каких условиях не является публичной офертой