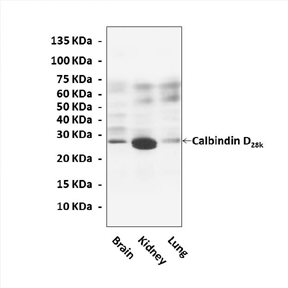
Anti-Calbindin D28k: Mouse Calbindin D28K Antibody |
 |
BACKGROUND Calbindin D belongs to the EF-hand family of calcium binding proteins and binds calcium ion with a fast association rate. It is widely expressed in Ca2+ transporting tissues such as epithelial-absorptive cells of the intestine and the distal tubular epithelial cells of the kidney. Calbindin-D was also found in the nervous system and it was suggested to co-localize with plasma membrane Ca2+ pumps. The function of Calbindin-D is dependent on the intracellular Ca2+ concentrations and it was shown that Ca2+ binding to Calbindin-D induced local structure changes around aromatic residues while no significant secondary structural changes were observed. In addition, Calbindin-D-containing neurons are thought to be related with memory, learning and long-term potentiation.1 It has been well known that Ca2+ plays a critical role in the light-mediated resetting of the circadian clock. Calbindin D influences Ca2+ buffering capacity of a cell, alters spatio-temporal aspects of intracellular Ca2+ signaling, and hence alters transmission of light information to the circadian clock in neurons of the suprachiasmatic nuclei (SCN).2 Moreover, Calbindin-D was also implicated in Parkinson’s disease (PD) since it was found that the dopaminergic neurons of the substantia nigra pars compacta (A9) expressing calbindin-D were more resistant to cell death than the neurons that do not express Calbindin-D in PD and in animal. In addition, alpha-Synuclein is a natively unfolded protein aggregation which is implicated in the pathogenesis of PD and several other neurodegenerative diseases, is known to interact with a great number of unrelated proteins. Some of these proteins, such as beta-synuclein and DJ-1, were shown to inhibit alpha-synuclein aggregation in vitro and in vivo therefore acting as chaperones. It was shown that Calbindin-D is also able to interact and co-aggregate with alpha-synuclein, significantly inhibiting alpha-synuclein fibrillation. Therefore, Calbindin-D28K can act as a chaperone, efficiently suppressing the process of alpha-synuclein fibril formation.3
REFERENCES
1. Lee, C.H. et al: Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 29:665–72, 2009
2. Stadler, F. et al: Chronobiol. Int. 27:68-82, 2010
3. Zhou, W. et al: Cent. Eur. J. Biol. • 5: 11–20, 2010
2. Stadler, F. et al: Chronobiol. Int. 27:68-82, 2010
3. Zhou, W. et al: Cent. Eur. J. Biol. • 5: 11–20, 2010
Products are for research use only. They are not intended for human, animal, or diagnostic applications.
Параметры
Cat.No.: | CA11007 |
Antigen: | Short peptide from human Calbindin D28k sequence. |
Isotype: | Mouse IgG1 |
Species & predicted species cross- reactivity ( ): | Human, Mouse, Rat |
Applications & Suggested starting dilutions:* | WB 1:1000 IP n/d IHC 1:50 - 1:200 ICC n/d FACS n/d |
Predicted Molecular Weight of protein: | 28 kDa |
Specificity/Sensitivity: | Detects endogenous levels of Calbindin D28k proteins without cross-reactivity with other related proteins. |
Storage: | Store at -20°C, 4°C for frequent use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
*Optimal working dilutions must be determined by end user.
Документы
Информация представлена исключительно в ознакомительных целях и ни при каких условиях не является публичной офертой