Anti-IFN-α: Monoclonal Interferon-alpha Antibody |
 |
BACKGROUND Interferon (IFN)-alpha and IFN-beta are critical mediators of host defense against microbial challenges, directly interfering with viral infection and influencing both the innate and adaptive immune responses. IFNs exert their effects in target cells through the activation of a cell-surface receptor, leading to a cascade of signaling events that determine transcriptional and translational regulation.1 Recombinant human IFN-alpha was the first biotherapeutic agent approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of a human malignancy. Its efficacy has also been demonstrated for treatment of several viral diseases including hepatitis.2,3
REFERENCES
1. Galligan, C.L. et al., Immunol. Res. 35:27, 2006.
2. Masci, P. et al., Curr. Oncol. Rep. 5:108, 2003.
3. Bukowaski, R. M. et al., Cancer 95:389, 2002.
2. Masci, P. et al., Curr. Oncol. Rep. 5:108, 2003.
3. Bukowaski, R. M. et al., Cancer 95:389, 2002.
Products are for research use only. They are not intended for human, animal, or diagnostic applications.
Параметры
Cat.No.: | CB10256 |
Antigen: | Recombinant human interferon-alpha protein |
Isotype: | Mouse Monoclonal IgG1 |
Species & predicted species cross- reactivity ( ): | Human |
Applications & Suggested starting dilutions: | WB 1:1000 IP n/d IHC n/d ICC n/d FACS n/d |
Predicted Molecular Weight of protein: | 19 kDa |
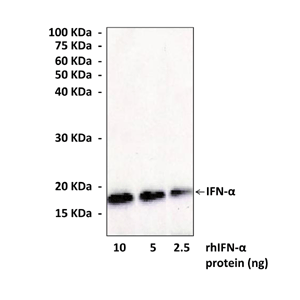
Specificity/Sensitivity: | Anti-IFN-alpha reacts specifically with human IFN-alpha in Western Blot applications. |
Storage: | -20° |
*Optimal working dilutions must be determined by end user.
Документы
Информация представлена исключительно в ознакомительных целях и ни при каких условиях не является публичной офертой