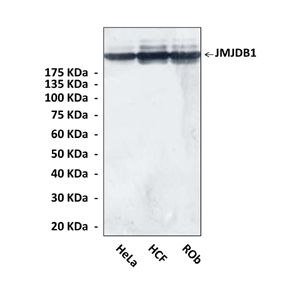
Anti-JMJD1B: Monoclonal JMJD1B Antibody |
 |
BACKGROUND The Jumonji (Jmj) gene was identified by a mouse gene trap approach and has essential roles in the development of multiple tissues. The Jmj protein has a DNA binding domain, ARID, and two conserved Jmj domains (JmjN and JmjC).
Several proteins in the Jumonji family are involved in transcriptional repression and/or chromatin regulation.1 Recently, human members of the family have been shown to be a histone demethylases, and the JmjC domain is essential for demethylase activity.2
Jumonji domain containing 1B (JMJD1B, also known as KDM3B/JHDM2B) contains a highly-conserved C-terminus, which includes a zinc finger with the unique spacing Cys-X2-Cys-X7-His-X2-Cys-X2-Cys-X4-Cys-X2-Cys and a JmjC domain. JMJD1B has been shown to be a histone demethylase responsible for demethylating mono methyl histone H3 at K9.3 Methylation of H3-K4 and H3-K9 is linked to transcriptional activation and repression, respectively. JMJD1B plays an important role in chromatin regulation and gene expression, and controls development through various signaling pathways. It may also be a candidate for tumor suppressors.
REFERENCES
REFERENCES
1. Jung J et al.: Dev Dyn. 232:21-32, 2005.
2. Shin S & Janknecht R: Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 353:973-7, 2007.
3. Natoli G et al.: Curr. Opin. Drug Dis. Dev. 12:607-615, 2009.
2. Shin S & Janknecht R: Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 353:973-7, 2007.
3. Natoli G et al.: Curr. Opin. Drug Dis. Dev. 12:607-615, 2009.
Products are for research use only. They are not intended for human, animal, or diagnostic applications.
Параметры
Cat.No.: | CC10021 |
Antigen: | Human JMJD1B C-terminal protein sequence. |
Isotype: | Mouse IgG2a |
Species & predicted species cross- reactivity ( ): | Human, Rat, Mouse |
Applications & Suggested starting dilutions: | WB 1:1000 IP 1:50 IHC 1:100 ICC n/d FACS n/d |
Predicted Molecular Weight of protein: | 195 kDa |
Specificity/Sensitivity: | Detects endogenous levels of JMJD1B protein in various cell lysates. |
Storage: | Store at 4° C for frequent use; at -20° C for at least one year. |
*Optimal working dilutions must be determined by end user.
Документы
Информация представлена исключительно в ознакомительных целях и ни при каких условиях не является публичной офертой