Anti-JNK3: Mouse JNK3/MAPK10 Antibody |
 |
BACKGROUND Members of the JNK family of kinases are activated by proinflammatory cytokines tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-1beta as well as environmental stress, such as anisomycin, UV irradiation, hypoxia and osmotic shock. Three distinct genes encoding JNKs, Jnk1, Jnk2 and Jnk3, have been identified and at least ten different splicing isoforms exist in mammalian cells. The downstream substrates of JNKs include the transcription factors c-Jun, ATF-2, Elk1, NFAT, p53 and a cell death domain protein. Each JNK isoform binds to these substrates with different affinities, suggesting a regulation of signaling pathways by substrate specificity of different JNKs in vivo. It was found that beta-arrestin 2, a receptor-regulated MAP kinase scaffold protein, can interact with JNK3, and stimulate the phosphorylation of this kinase by MAP kinase kinase 4 (MKK4).1 Cyclin-dependent kianse 5 can phosphorylate, and inhibit the activity of this kinase, which may be important in preventing neuronal apoptosis.2
JNK1 and JNK2 are widely expressed in a variety of tissues. In contrast, JNK3 is selectively expressed in the brain and to a lesser extent in the heart and testis. In the adult human brain, JNK3 expression is localized to a subpopulation of pyramidal neurons in the CA1, CA4 and subiculum regions of the hippocampus and layers 3 and 5 of the neocortex. The CA1 neurons in brain biopsies of patients diagnosed with acute hypoxia showed strong nuclear JNK3 immunoreactivity. In contrast, control samples taken from patients with nonneuronal diseases revealed only diffused cytoplasmic JNK3 staining in the hippocampal neurons. Furthermore, disruption of the JNK3 gene caused resistance of mice to the excitotoxic glutamate receptor agonist kainic acid, including the effects on seizure activity, AP-1 transcriptional activity and apoptosis of hippocampal neurons, indicating that the JNK3 signaling pathway is a critical component in the pathogenesis of glutamate neurotoxicity. Thus, selective modulation of JNK3 activity could potentially provide therapeutic intervention for neurodegenerative diseases such as stroke and epilepsy.3
REFERENCES
1. Scapin, G. et al: Chem. Biol. 10:705-12, 2003
2. Saporito, MS. Et al: J. Neurosci. 75:1200-8, 2002
3. Xie, X. et al: Structure 6:983-91, 1998
2. Saporito, MS. Et al: J. Neurosci. 75:1200-8, 2002
3. Xie, X. et al: Structure 6:983-91, 1998
Products are for research use only. They are not intended for human, animal, or diagnostic applications.
Параметры
Cat.No.: | CP10162 |
Antigen: | Purified recombinant human JNK3 fragments expressed in E. coli. |
Isotype: | Mouse IgG1 |
Species & predicted species cross- reactivity ( ): | Human, Mouse |
Applications & Suggested starting dilutions:* | WB 1:1000 IP n/d IHC n/d ICC 1:200 FACS n/d |
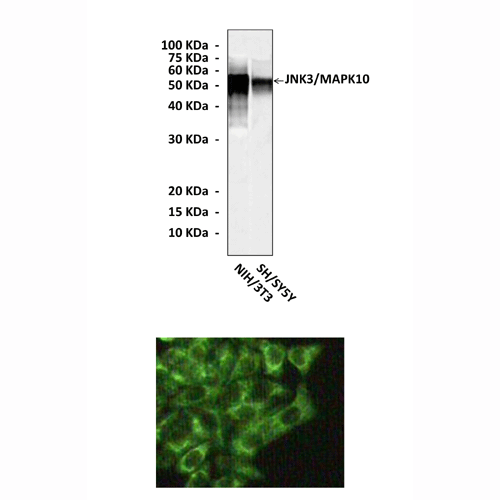
Predicted Molecular Weight of protein: | 54 kDa |
Specificity/Sensitivity: | Detects endogenous JNK3/MAPK10 proteins without cross-reactivity with other family members. |
Storage: | Store at -20°C, 4°C for frequent use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
*Optimal working dilutions must be determined by end user.
Документы
Информация представлена исключительно в ознакомительных целях и ни при каких условиях не является публичной офертой