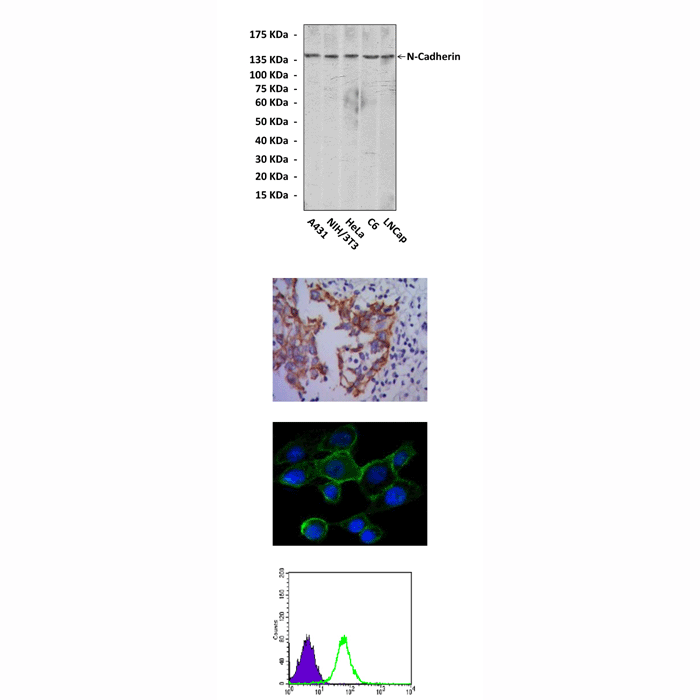
Anti-N-Cadherin: Mouse N-Cadherin Antibody |
 |
BACKGROUND Cell adhesion molecules (CAMs) are cell surface proteins that are involved in cell-cell and cell-matrix interactions during embryonic development and in the maintenance of the tissue architecture of mature organisms. CAMs can be broadly grouped into four distinct families based on their structure and sequence homologies: integrins, the immunoglobulin-gene family, selectins and cadherins. Cadherins are calcium-dependent transmembrane glycoproteins that mediate cell-cell adhesion. The classic cadherin subfamily includes N-, P-, R-, B- and E-cadherins as well as about ten other members which are found in adherens junctions (AJ).1 These proteins share a common basic structure. The extracellular portions of the proteins are largely composed of repeating domains, each with two concensus Ca2+ binding motifs. The intracellular domain, the most conserved region of these molecules, is associated with cytoskeletal elements via cytoplasmic proteins termed catenins (alpha, beta, and gamma) and plays a central role in cadherin function.2 Cadherins are the most important cell-cell receptors for the formation of physical cell-cell association and maintenance of normal tissue morphology.
N-cadherin is expressed in various neuronal cells as well as in glial cells of the central and peripheral nervous systems in vertebrate embryos and recent immunological studies suggested that N-cadherin may play a role in guiding the migration of neurites on myotubes or astrocytes.3 It also found that eoverexpression of N-cadherin is some tumor cells promoted cell migration, invasion, and metastasis.4
N-cadherin is expressed in various neuronal cells as well as in glial cells of the central and peripheral nervous systems in vertebrate embryos and recent immunological studies suggested that N-cadherin may play a role in guiding the migration of neurites on myotubes or astrocytes.3 It also found that eoverexpression of N-cadherin is some tumor cells promoted cell migration, invasion, and metastasis.4
REFERENCES
1. Leckband D & Prakasam A: Ann. Rev. Biomed. Engin. 8:259-287,2006
2. Alattia JR et al.: Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 55: 359-367, 1999.
3. Matsunaga, M. et al: nature 334:62-64, 1988
4. Hazan, R.B. et al: J. Cell Biol. 148:779-790, 2000
2. Alattia JR et al.: Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 55: 359-367, 1999.
3. Matsunaga, M. et al: nature 334:62-64, 1988
4. Hazan, R.B. et al: J. Cell Biol. 148:779-790, 2000
Products are for research use only. They are not intended for human, animal, or diagnostic applications.
Параметры
Cat.No.: | CP10300 |
Antigen: | Raised against recombinant human intracellular N-Cadherin fragments expressed in E. coli. |
Isotype: | Mouse IgG1 |
Species & predicted species cross- reactivity ( ): | Human, Mouse, Rat |
Applications & Suggested starting dilutions:* | WB 1:1000 IP 1:50 IHC 1:50 - 1:200 ICC 1:50 - 1:200 FACS 1:50 - 1:200 |
Predicted Molecular Weight of protein: | 140 kDa |
Specificity/Sensitivity: | Detects endogenous N-Cadherin proteins without cross-reactivity with other family members. |
Storage: | Store at -20°C, 4°C for frequent use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
*Optimal working dilutions must be determined by end user.
Документы
Информация представлена исключительно в ознакомительных целях и ни при каких условиях не является публичной офертой