BMP-2 ELISA Kit, Rat |
 |
BACKGROUND Bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs) are members of the transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) family that play essential roles in osteogenesis. BMPs play a pivotal role in the commitment and differentiation of cells of osteoblastic lineage. BMP-2, a prototype of BMPs, promotes osteoblast maturation by increasing the expression of the transcription factor Runx2 (also called Cbfa1/Pebp-alphaA/AML3), and the expression of osteoblast marker genes. In addition to bone formation, It has been shown that BMP-2 plays pivotal roles in cell proliferation, apoptosis, and differentiation. In non-skeletal cell types, BMPs were found to regulate apoptosis, although both pro- and antiapoptotic effects have been reported. Furthermore, it was reported that BMP-2 induces growth arrest in mouse B-cell hybridoma HS-72 cells and in human myeloma cells.1
BMPs signal through type I and II serine/threonine kinase receptors that phosphorylate the downstream target proteins Smads. Activation of type I BMP receptor phosphorylates Smad1, Smad5, and presumably Smad8 and associates with Smad4 in a heteromeric complex that is translocated to the nucleus, where it activates transcription. TGF-beta binding to receptors leads to phosphorylated Smad2 and Smad3, which associate with Smad4, and the complex can translocate to the nucleus to regulate transcriptional activity. The Smad signaling pathway has been shown to play a role in BMP-2-induced osteoblast differentiation. However, other signaling pathways, such as extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK1/2), protein kinase C, and cAMP-dependent protein kinase A (PKA) may also be involved in the BMP-induced effects on bone cells. It was shown that PI-3 kinase/Akt pathway was involved in BMP-2 induced osteoblast differentiation.2 Another cascade is activated by TGF-beta and BMP-4 and involves TGF-beta-activated kinase-1 (TAK1), a member of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) kinase family, p38, and c-Jun N-terminal kinase. The TAK1-p38 kinase pathway was also found to be involved in BMP-2-induced apoptosis. It was also shown that that the BMP-2-induced apoptosis in human osteoblasts is mediated by activation of PKC, leading to activation of caspase-9, effector caspases, and DNA fragmentation.3 Moreover, BMP-2 mediates retinoid-induced apoptosis in medulloblastoma cells through a paracrine effect.4 Additionally, it was shown that BMP-2 signaling may cross-talk with Wnt signaling pathway in regulation of C2C12 cell differentiation.5
BMPs signal through type I and II serine/threonine kinase receptors that phosphorylate the downstream target proteins Smads. Activation of type I BMP receptor phosphorylates Smad1, Smad5, and presumably Smad8 and associates with Smad4 in a heteromeric complex that is translocated to the nucleus, where it activates transcription. TGF-beta binding to receptors leads to phosphorylated Smad2 and Smad3, which associate with Smad4, and the complex can translocate to the nucleus to regulate transcriptional activity. The Smad signaling pathway has been shown to play a role in BMP-2-induced osteoblast differentiation. However, other signaling pathways, such as extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK1/2), protein kinase C, and cAMP-dependent protein kinase A (PKA) may also be involved in the BMP-induced effects on bone cells. It was shown that PI-3 kinase/Akt pathway was involved in BMP-2 induced osteoblast differentiation.2 Another cascade is activated by TGF-beta and BMP-4 and involves TGF-beta-activated kinase-1 (TAK1), a member of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) kinase family, p38, and c-Jun N-terminal kinase. The TAK1-p38 kinase pathway was also found to be involved in BMP-2-induced apoptosis. It was also shown that that the BMP-2-induced apoptosis in human osteoblasts is mediated by activation of PKC, leading to activation of caspase-9, effector caspases, and DNA fragmentation.3 Moreover, BMP-2 mediates retinoid-induced apoptosis in medulloblastoma cells through a paracrine effect.4 Additionally, it was shown that BMP-2 signaling may cross-talk with Wnt signaling pathway in regulation of C2C12 cell differentiation.5
REFERENCES
1. Reddi, A.H.: Cytokine Growth Fact. Rev.8:11-20, 1997
2. Ghosh-Choudhury, N. et al: J. Biol. Chem 277:33361-8, 2002
3. Hay, E. et al: J. Biol. Chem. 276:29028-36, 2001
4. Hallahan, A.R. et al: Nat. Med. 9:1033-8, 2003
5. Nakashima, A. et al: J. Biol. Chem. 280:37760-8, 2005
2. Ghosh-Choudhury, N. et al: J. Biol. Chem 277:33361-8, 2002
3. Hay, E. et al: J. Biol. Chem. 276:29028-36, 2001
4. Hallahan, A.R. et al: Nat. Med. 9:1033-8, 2003
5. Nakashima, A. et al: J. Biol. Chem. 280:37760-8, 2005
Products are for research use only. They are not intended for human, animal, or diagnostic applications.
Параметры
Cat.No.: | CL0312 |
Target Protein Species: | Rat |
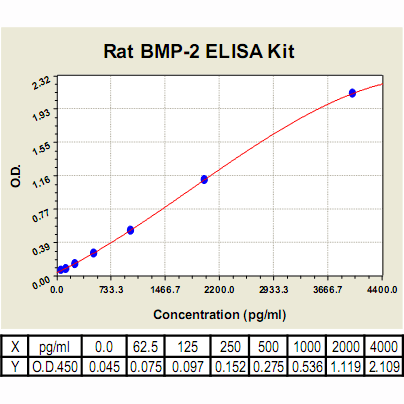
Range: | 62.5pg/ml – 4000 pg/ml |
Specificity: | No detectable cross-reactivity with other cytokines |
Storage: | Store at 4°C. Use within 6 months. |
ELISA Kits are based on standard sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay technology. Freshly prepared standards, samples, and solutions are recommended for best results.
Документы
Информация представлена исключительно в ознакомительных целях и ни при каких условиях не является публичной офертой