BMP-4 ELISA Kit, Human |
 |
BACKGROUND Bone morphogenetic protein 4 (BMP-4) is a polypeptide belonging to the TGF-bTGF superfamily of proteins. Like other bone morphogenetic proteins, BMP-4 is involved in bone and cartilage development, specifically tooth and limb development and fracture repair. It has been shown to be involved in muscle development, bone mineralization, and uteric bud development.1 In human embryonic development, BMP-4 is a critical signaling molecule required for the early differentiation of the embryo and establishment of a dorsal-ventral axis. BMP-4 is secreted from the dorsal portion of the notochord, and it acts in concert with sonic hedgehog (released from the ventral portion of the notochord) to establish a dorsal-ventral axis for the differentiation of later structures.2 BMP-4 stimulates differentiation of overlying ectodermal tissue.3 Inhibition of the BMP-4 signal (by chordin, noggin, or follistatin) causes the ectoderm to differentiate into the neural plate. If these cells also receive signals from FGF, they will differentiate into the spinal cord; in the absence of FGF the cells become brain tissue.
REFERENCES
1. Chen, D. et al., Growth Factors 22:233, 2004.
2. Aberdam, D. et al., Bull. Acad. Natl. Med. 189:645, 2005.
3. Czyz, J. & Wobus, A., Differentiation 68:167, 2001.
2. Aberdam, D. et al., Bull. Acad. Natl. Med. 189:645, 2005.
3. Czyz, J. & Wobus, A., Differentiation 68:167, 2001.
Products are for research use only. They are not intended for human, animal, or diagnostic applications.
Параметры
Cat.No.: | CL0314 |
Target Protein Species: | Human |
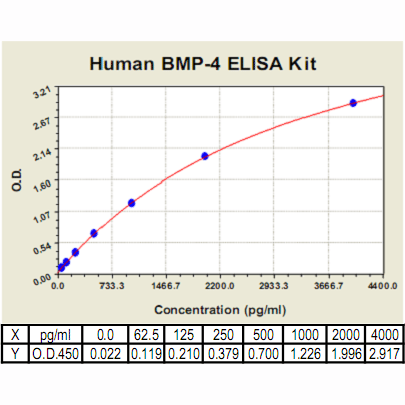
Range: | 62.5pg/ml – 4000 pg/ml |
Specificity: | No detectable cross-reactivity with other cytokines |
Storage: | Store at 4°C. Use within 6 months. |
ELISA Kits are based on standard sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay technology. Freshly prepared standards, samples, and solutions are recommended for best results.
Документы
Информация представлена исключительно в ознакомительных целях и ни при каких условиях не является публичной офертой