Leptin ELISA Kit, Human |
 |
BACKGROUND Leptin is the hormonal product of the obese (ob) gene and is expressed by adipocytes. The level of circulating leptin is directly proportional to the total amount of fat in the body.1 It plays a role in the regulation of food intake and metabolism. Leptin acts on receptors in the hypothalamus of the brain. It counteracts the effects of neuropeptide Y and anandamide , both are potent feeding stimulants. Moreover, it promotes the synthesis of α-MSH, an appetite suppressant. Thus,food intake was inhibited. The absence of a functional hormone (or its receptor) leads to uncontrolled food intake and resulting obesity. Leptin also acts on hypothalamic neurons responsible for the secretion of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) and stimulating the sympathetic nervous system to modulate the balance between the formation and breakdown of bone.2 In addition to its effect on the hypothalamus, leptin acts directly on the cells of the liver and skeletal muscle where it stimulates the oxidation of fatty acids in the mitochondria. This reduces the storage of fat in those tissues (but not in adipose tissue). It also acts on T cells where it enhances the production of Th1 cells promoting inflammation. Mice without leptin are protected from autoimmune disease.3 Mutations in the gene for leptin, or in its receptor, are rarely found in obese people.
REFERENCES
1. Houseknecht, K. H. et al: J. Anim. Sci. 76:1405-20, 1998
2. Margetic, S. et al: Int. J. Obesity 26:1407-1433, 2002
3. Ahima, R.S. & Flier, J.S.: Ann. Rev. Physiol. 62:413-437, 2000
2. Margetic, S. et al: Int. J. Obesity 26:1407-1433, 2002
3. Ahima, R.S. & Flier, J.S.: Ann. Rev. Physiol. 62:413-437, 2000
Products are for research use only. They are not intended for human, animal, or diagnostic applications.
Параметры
Cat.No.: | CL0437 |
Target Protein Species: | Human |
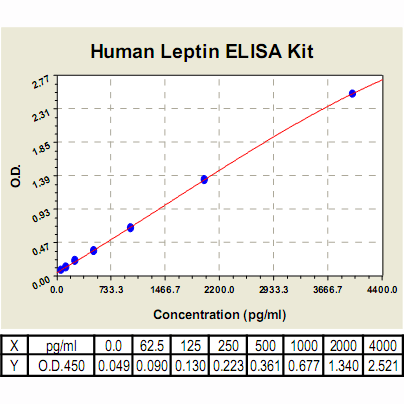
Range: | 62.5 pg/ml – 4000pg/ml |
Specificity: | No detectable cross-reactivity with IGF-1 |
Storage: | Store at 4°C. Use within 6 months. |
ELISA Kits are based on standard sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay technology. Freshly prepared standards, samples, and solutions are recommended for best results.
Документы
Информация представлена исключительно в ознакомительных целях и ни при каких условиях не является публичной офертой