Anti-Akt2: Mouse Akt2 Antibody |
 |
BACKGROUND AKT, also called protein kinase B (PKB), is a serine/threonine-specific protein kinase originally identified as the oncogene in the transforming retrovirus, AKT8. It plays an important role in mammalian cellular signaling.1 In humans, the Akt family has three members: Akt1, Akt2, and Akt3. Akt1 is involved in cellular survival pathways by inhibiting apoptotic processes. Akt1 is also able to induce protein synthesis pathways, and is therefore a key signaling protein in the cellular pathways that lead to skeletal muscle hypertrophy, and general tissue growth. Since it can block apoptosis, and thereby promote cell survival, Akt1 has been implicated as a major factor in many types of cancer.2 Akt2 is an important signaling molecule in the insulin signaling pathway. It is required to induce glucose transport.3 The role of Akt3 is less clear, though it appears to be predominantly expressed in the brain. It has been reported that mice lacking Akt3 have small brains.4
REFERENCES
1. Chan T et al.: Annu. Rev. Biochem. 68:965-1014, 1999.
2. Bussink J et al.: Lancet Oncol. 9:288-296, 2008.
3. Ng Y et al.: Cell Metabolism, 7: 348-356, 2008.
4. Easton RM et al.: Mol Cell Biol. 25: 1869–1878, 2005
2. Bussink J et al.: Lancet Oncol. 9:288-296, 2008.
3. Ng Y et al.: Cell Metabolism, 7: 348-356, 2008.
4. Easton RM et al.: Mol Cell Biol. 25: 1869–1878, 2005
Products are for research use only. They are not intended for human, animal, or diagnostic applications.
Параметры
Cat.No.: | CP10006 |
Antigen: | Recombinant human Akt2 protein fragment expressed in E. coli. |
Isotype: | Mouse IgG2b |
Species & predicted species cross- reactivity ( ): | Human, Mouse, Rat |
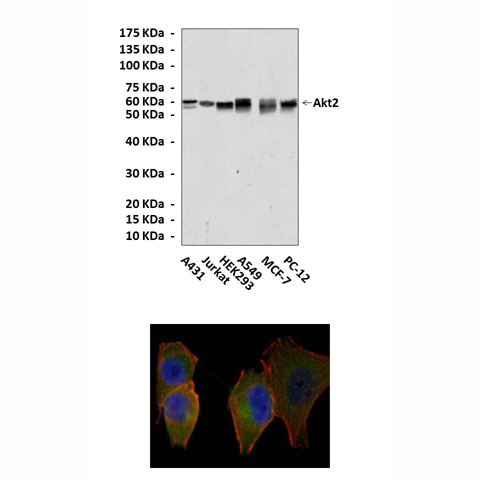
Applications & Suggested starting dilutions:* | WB 1:1000 IP 1:50 IHC 1:200 |
Predicted Molecular Weight of protein: | 60 kDa |
Specificity/Sensitivity: | Detects endogenous levels of Akt2 proteins in normal cell lysates without cross-reactivity with other family members. |
Storage: | Store at -20°C, 4°C for frequent use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
*Optimal working dilutions must be determined by end user.
Документы
Информация представлена исключительно в ознакомительных целях и ни при каких условиях не является публичной офертой