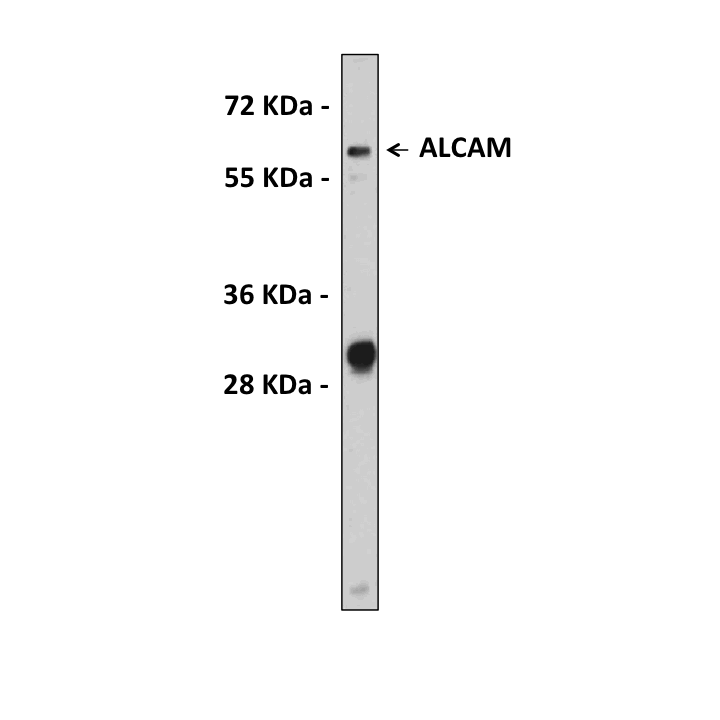
Anti-ALCAM: Rabbit Activated Leucocyte Cell Adhesion Antibody |
 |
BACKGROUND ALCAM (activated leucocyte cell adhesion molecule, synonym CD166) is a cell adhesion molecule, which belongs to the Ig superfamily. It binds to CD6. Its function is involved in neurite extension by neurons via heterophilic and homophilic interactions. ALCAM may play a role in the binding of T- and B-cells to activated leukocytes, as well as in interactions between cells of the nervous system.1 For clinical studies, ALCAM is a valuable prognostic and predictive marker in several types of epithelial tumors. Disruption of the ALCAM-mediated adhesiveness by proteolytic sheddases such as ADAM17 has been suggested to have a relevant impact on tumor invasion.2
REFERENCES
1. Bowen, M.A. et al: J. Biol. Chem. 271:17390-6, 1996
2. Weichert, W. et al: J. Clin. Pathol. 57:1160-64, 2004
2. Weichert, W. et al: J. Clin. Pathol. 57:1160-64, 2004
Products are for research use only. They are not intended for human, animal, or diagnostic applications.
Параметры
Cat.No.: | CG1653 |
Antigen: | Immunogen Sequence: EK PDGSPVFIAF RSSTKKSVQY DDVPEYK |
Isotype: | Rabbit IgG |
Species & predicted species cross- reactivity ( ): | Human |
Applications & Suggested starting dilutions:* | WB 1:1000 IP n/d IHC 1:50-1:100 ICC 1:10-1:50 FACS n/d |
Predicted Molecular Weight of protein: | 65102 Da |
Specificity/Sensitivity: | Detects endogenous ALCAM proteins without cross-reactivity with other family members. |
Storage: | Store at -20°C, 4°C for frequent use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
*Optimal working dilutions must be determined by end user.
Документы
Информация представлена исключительно в ознакомительных целях и ни при каких условиях не является публичной офертой