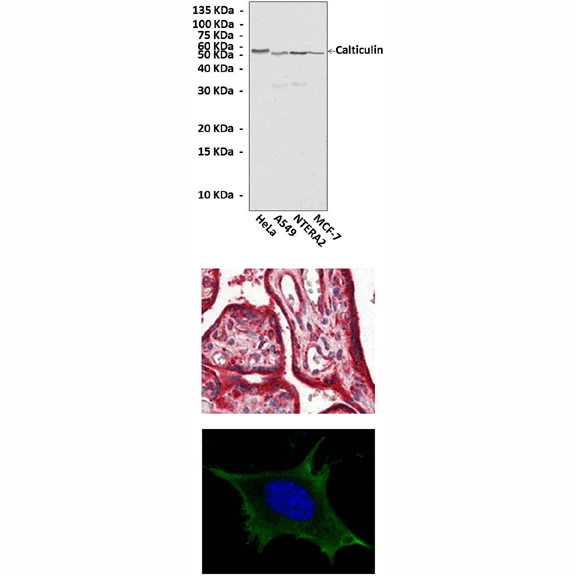
Anti-Calreticulin: Mouse Calreticulin Antibody |
 |
BACKGROUND Calreticulin is a multifunctional protein that acts as a major Ca2+-binding (storage) protein in the lumen of the Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER). ER plays a critical role in the synthesis and chaperoning of membrane-associated and secreted proteins. The membrane is also an important site of Ca2+ storage and release. Calreticulin is a unique ER luminal resident protein. The protein affects many cellular functions, both in the ER lumen and outside of the ER environment. In the ER lumen, Calreticulin performs two major functions: chaperoning and regulation of Ca2+ homoeostasis. Calreticulin is a highly versatile lectin-like chaperone, and it participates during the synthesis of a variety of molecules, including ion channels, surface receptors, integrins and transporters. The protein also affects intracellular Ca2+ homoeostasis by modulation of ER Ca2+ storage and transport.1 Studies on the cell biology of Calreticulin revealed that the ER membrane is a very dynamic intracellular compartment affecting many aspects of cell physiology.
Calreticulin is also found in the nucleus, suggesting that it may have a role in transcription regulation. Calreticulin binds to the synthetic peptide KLGFFKR, which is almost identical to an amino acid sequence in the DNA-binding domain of the superfamily of nuclear receptors. The amino terminus of Calreticulin interacts with the DNA-binding domain of the glucocorticoid receptor and prevents the receptor from binding to its specific glucocorticoid response element. Calreticulin can inhibit the binding of androgen receptor to its hormone-responsive DNA element and can inhibit androgen receptor and retinoic acid receptor transcriptional activities in vivo, as well as retinoic acid-induced neuronal differentiation. Thus, Calreticulin can act as an important modulator of the regulation of gene transcription by nuclear hormone receptors.2 In addition calticulin may be involved in some disease development. Systemic lupus erythematosus is associated with increased autoantibody titers against Calreticulin but Calreticulin is not a Ro/SS-A antigen.3
Calreticulin is also found in the nucleus, suggesting that it may have a role in transcription regulation. Calreticulin binds to the synthetic peptide KLGFFKR, which is almost identical to an amino acid sequence in the DNA-binding domain of the superfamily of nuclear receptors. The amino terminus of Calreticulin interacts with the DNA-binding domain of the glucocorticoid receptor and prevents the receptor from binding to its specific glucocorticoid response element. Calreticulin can inhibit the binding of androgen receptor to its hormone-responsive DNA element and can inhibit androgen receptor and retinoic acid receptor transcriptional activities in vivo, as well as retinoic acid-induced neuronal differentiation. Thus, Calreticulin can act as an important modulator of the regulation of gene transcription by nuclear hormone receptors.2 In addition calticulin may be involved in some disease development. Systemic lupus erythematosus is associated with increased autoantibody titers against Calreticulin but Calreticulin is not a Ro/SS-A antigen.3
REFERENCES
1. Michalak, M. et al: Biochem. J. 344:281-292, 1999
2. Burns, K. et al: Nature 367:476-80, 1994
3. Eggleton, P. :Lupus 6:564-71, 1997
2. Burns, K. et al: Nature 367:476-80, 1994
3. Eggleton, P. :Lupus 6:564-71, 1997
Products are for research use only. They are not intended for human, animal, or diagnostic applications.
Параметры
Cat.No.: | CP10033 |
Antigen: | Short peptide (EEEDVPGQAKDELC) from human Calreticulin sequence. |
Isotype: | Mouse IgG2a |
Species & predicted species cross- reactivity ( ): | Human, Mouse, Rat |
Applications & Suggested starting dilutions:* | WB 1:1000 IP 1:25 - 1:50 IHC 1:100 - 1:250 ICC 1:100 - 1:250 FACS n/d |
Predicted Molecular Weight of protein: | 55 kDa |
Specificity/Sensitivity: | Detects endogenous Calreticulin proteins in normal cell lysates without cross-reactivity with other related proteins. |
Storage: | Store at -20°C, 4°C for frequent use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
*Optimal working dilutions must be determined by end user.
Документы
Информация представлена исключительно в ознакомительных целях и ни при каких условиях не является публичной офертой