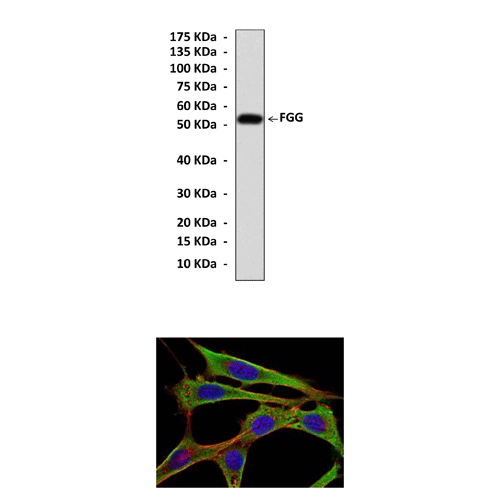
Anti-FGG: Mouse Fibrinogen-gamma Antibody |
 |
BACKGROUND Fibrinogen gamma chain, also known as FGG, is a human gene found on Chromosome 4. The protein encoded by this gene is the gamma component of fibrinogen, a blood-borne glycoprotein composed of three pairs of nonidentical polypeptide chains. Following vascular injury, fibrinogen is cleaved by thrombin to form fibrin which is the most abundant component of blood clots.1 In addition, various cleavage products of fibrinogen and fibrin regulate cell adhesion and spreading, display vasoconstrictor and chemotactic activities, and are mitogens for several cell types. Mutations in this gene lead to several disorders, including dysfibrinogenemia, hypofibrinogenemia and thrombophilia.2 Alternative splicing of the mRNA chain results in two transcript variants; the common γA chain and the alternatively spliced γ' chain. Approximately 10% of the total plasma fibrinogen consists of γA/γ' fibrinogen, with <1% consisting of γ'/γ' fibrinogen. Increased and decreased levels of γA/γ' fibrinogen have been associated with CAD and DVT respectively.
REFERENCES
1. Doolittle, R.F. et al: Annu. Rev. Biochem. 53: 195–229, 1984
2. Scott, E.M. et al: Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 24: 1558–66, 2005
Products are for research use only. They are not intended for human, animal, or diagnostic applications.
Параметры
Cat.No.: | CP10404 |
Antigen: | Raised against recombinant human FGG fragments expressed in E. coli. |
Isotype: | Mouse IgG1 |
Species & predicted species cross- reactivity ( ): | Human, Mouse, Rat |
Applications & Suggested starting dilutions:* | WB 1:1000 IP 1:50 IHC n/d ICC 1:50 - 1:200 FACS n/d |
Predicted Molecular Weight of protein: | 52 kDa |
Specificity/Sensitivity: | Detects FGG proteins in various cell lysate. |
Storage: | Store at -20°C, 4°C for frequent use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
*Optimal working dilutions must be determined by end user.
Документы
Информация представлена исключительно в ознакомительных целях и ни при каких условиях не является публичной офертой