Anti-Fibulin-5: Mouse Fibulin-5 Antibody |
 |
BACKGROUND Fibulins constitute a small family of five extracellular matrix proteins that share a distinctive carboxyl-terminal globular domain and a tandem array of calcium-binding epidermal growth factor-like modules. They bind various extracellular ligands including fibronectin and calcium. They play important role during organ development, in particular, during the differentiation of heart, skeletal and neuronal structures. The fibulins not only share structural similarities but also have overlapping expression patterns. A notable common feature is that all fibulins are abundantly distributed in elastic tissues.1 The biological roles of most fibulins have been elucidated through studies of gene-targeted mouse models.2
Fibulin-5 belongs to the fibulin ECM family, which consists of six members characterized by tandem repeats of calcium binding epidermal growth factor (EGF)-like (CB-EGF) domains and a C-terminal fibulin module. Fibulin-1, -2, -4, and -5 colocalize with elastic fibers and bind tropoelastin, whereas the elastic fiber binding properties of fibulin-3 have not been determined. In addition to tropoelastin, Fibulin-5 was shown to bind N-terminal fragments of fibrillin-1 without interfering with either the homophilic interaction of fibrillin-1 or the heterotypic interaction of fibrillin-1 with tropoelastin. Binding of Fibulin-5 to the integrin receptors Vbeta3, Vbeta5, and 9beta1 in adhesion assays suggests that Fibulin-5 may serve to anchor tropoelastin to surrounding cells during assembly and/or final organization of functional elastic fibers. Fibulin-5 is also capable of tethering extracellular enzymes to elastic fibers. For example, Fibulin-5 appears to be required for the correct localization of lysyl oxidase like-1 (LOXL-1), an elastin cross-linking enzyme critical for maintenance of elastic fiber homeostasis in adult mice. Fibulin-2 and Fibulin-5 cooperatively function to form the internal elastic lamina during postnatal development by directing the assembly of elastic fibers, and are responsible for maintenance of the adult vessel wall after injury.3
REFERENCES
1. Zhang, R.Z. et al: Genomics 22:425-30, 1994
2. Sicot, F.-X. et al: Mol. Cell. Biol. 28:1061-7, 2008
3. Chapman, S.L. et al: Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology 30:68-74, 2010
2. Sicot, F.-X. et al: Mol. Cell. Biol. 28:1061-7, 2008
3. Chapman, S.L. et al: Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology 30:68-74, 2010
Products are for research use only. They are not intended for human, animal, or diagnostic applications.
Параметры
Cat.No.: | CP10098 |
Antigen: | Purified recombinant human Fibulin-5 fragment expressed in E. coli. |
Isotype: | Mouse IgG |
Species & predicted species cross- reactivity ( ): | Human, Mouse, Rat |
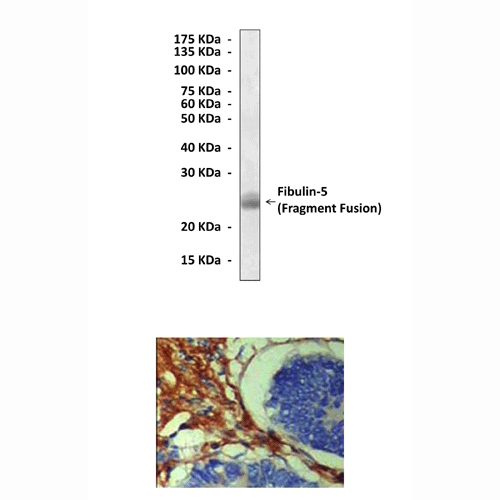
Applications & Suggested starting dilutions:* | WB 1:1000 IP n/d IHC 1:200 ICC n/d FACS n/d |
Predicted Molecular Weight of protein: | 60 kDa |
Specificity/Sensitivity: | Detects Fibulin-5 proteins without cross-reactivity with other family members. |
Storage: | Store at -20°C, 4°C for frequent use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
*Optimal working dilutions must be determined by end user.
Документы
Информация представлена исключительно в ознакомительных целях и ни при каких условиях не является публичной офертой