Anti-Cytochrome C: Polyclonal Cytochrome C Antibody |
 |
BACKGROUND Cytochromes c (cyt c) is a memeber of family of electron¬transfer proteins having one or several haem c groups, bound to the protein by one or, more commonly two, thioether bonds involving sulphydryl groups of cysteine residues. The fifth haem iron ligand is always provided by a histidine residue. Cyt c possess a wide range of properties and function in a large number of different redox processes.1 It is primarily known for its function in the mitochondria as a key participant in the life-supporting function of ATP synthesis. However, when a cell receives an apoptotic stimulus, cytochrome c is released into the cytosol and triggers programmed cell death through apoptosis. The release of cytochrome c and cytochrome-c-mediated apoptosis are controlled by multiple layers of regulation, the most prominent players being members of the B-cell lymphoma protein-2 (BCL2) family.2 As well as its role in canonical intrinsic apoptosis, cytochrome c amplifies signals that are generated by other apoptotic pathways and participates in certain non-apoptotic functions.3
REFERENCES
1. Adman ET: Biochim. Biophys. Acta 549:107-144, 1979.
2. Jiang X & Wang X: Ann. Rev. Biochem., 73: 87-106, 2004.
3. Ow YLP et al.: Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 9:532-542, 2008.
2. Jiang X & Wang X: Ann. Rev. Biochem., 73: 87-106, 2004.
3. Ow YLP et al.: Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 9:532-542, 2008.
Products are for research use only. They are not intended for human, animal, or diagnostic applications.
Параметры
Cat.No.: | CC1042 |
Antigen: | Sequence near the human Cytochrome C N-terminal. |
Isotype: | Affinity purified rabbit IgG |
Species & predicted species cross- reactivity ( ): | Human, Mouse, Rat |
Applications & Suggested starting dilutions: | WB 1:1000 IP n/d IHC (Paraffin) n/d ICC n/d FACS n/d |
Predicted Molecular Weight of protein: | 14 kDa |
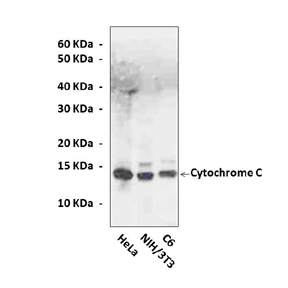
Specificity/Sensitivity: | Detects detects endogenous Cytochrome C proteins in various cell lysates. |
Storage: | Store at 4° C for frequent use; at -20° C for at least one year. |
*Optimal working dilutions must be determined by end user.
Документы
Информация представлена исключительно в ознакомительных целях и ни при каких условиях не является публичной офертой