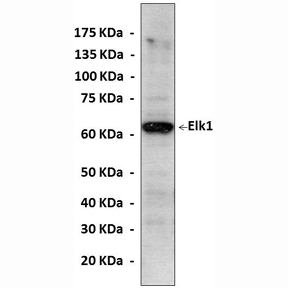
Anti-Elk1: Mouse Elk1 Antibody |
 |
BACKGROUND Elk1 is a member of ETS-domain transcription factor family. ETS proteins form one of the largest families of signal-dependent transcriptional regulators, mediating cellular proliferation, differentiation and tumorigenesis.1 Elk-1 is regulated by phosphorylation in response to activation of the MAPK (mitogen-activated protein kinase) pathways. This phosphorylation triggers a series of molecular events that convert Elk-1 from a transcriptionally silent state into a highly active state and then back to a basal level.2 At the same time, activation of the ERK (extracellular-signal-regulated kinase) MAPK pathway leads to loss of modification of Elk-1 by SUMO (small ubiquitin-related modifier). As SUMO imparts repressive properties on Elk-1, ERK-mediated SUMO loss leads to de-repression at the same time as the ERK pathway promotes activation of Elk-1.3 Thus a two-step mechanism is employed to convert Elk-1 into its fully activated state.
REFERENCES
1. Tsu, T. et al.: J. Cell. Biochem. 91:896, 2004.
2. Yang, S. H. & Sharrocks, A. D.: Biochem. Soc. Symp. 73:121, 2006.
3. Yang, S. H. et al.: Mol. Cell 12:63, 2003.
2. Yang, S. H. & Sharrocks, A. D.: Biochem. Soc. Symp. 73:121, 2006.
3. Yang, S. H. et al.: Mol. Cell 12:63, 2003.
Products are for research use only. They are not intended for human, animal, or diagnostic applications.
Параметры
Cat.No.: | CB13452 |
Antigen: | E. coli-expressed recombinant human Elk1 protein. |
Isotype: | Mouse Monoclonal IgG1 |
Species & predicted species cross- reactivity ( ): | Human, Mouse, Rat |
Applications & Suggested starting dilutions:* | WB 1:1000 IP n/d IHC n/d ICC n/d FACS n/d |
Predicted Molecular Weight of protein: | 62 kDa |
Specificity/Sensitivity: | Detects Elk1 protein and does not cross-react with related proteins. |
Storage: | Store at -20°C, 4°C for frequent use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
*Optimal working dilutions must be determined by end user.
Документы
Информация представлена исключительно в ознакомительных целях и ни при каких условиях не является публичной офертой