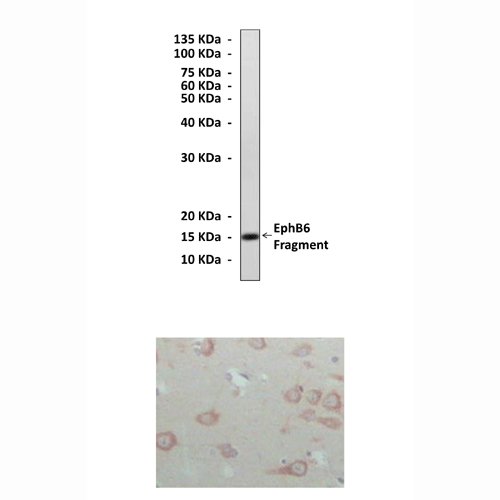
Anti-EphB6: Mouse EphB6 Antibody |
 |
BACKGROUND Eph family of receptor tyrosine kinases consists of at least 14 distinct receptors and has eight membrane-bound ligands, known as the ephrins. This is the largest family of receptor tyrosine kinases. Eph proteins are divided into two subfamilies: the EphA receptors (A1-A8) that bind glycosyl phosphatidylinositol (GPI)-linked ephrin-A ligands (A1-A5), and the EphB receptors (B1-B6) that bind transmembrane ephrin-B ligands (B1-B3). The only known crosstalk between the A and B subfamilies occurs with the EphA4 receptor, which can bind ephrins-B2 and -B3 as well as the entire A subclass. There is a great deal of redundancy of receptor-ligand binding specificity within each subfamily, although binding affinities vary.1,2 Both GPI-anchoredephrinA and transmembrane ephrinB ligands interact with the Nterminal globular domain (Glob) of Eph receptors. The Eph receptors become phosphorylated at specific tyrosine residues in the cytoplasmic domain following ligand binding. Phosphorylated motifs serve as sites of interaction with certain cytoplasmic signaling proteins to mediate downstream signaling. In addition, through their C terminus the Eph receptors associate with PDZ (postsynaptic density protein, disc large, zona occludens) domain-containing proteins. Moreover, Eph receptor contact induces tyrosine phosphorylation of the cytoplasmic domain of ephrinB proteins via an SRC-family kinase (SFK), which mediating the reverse signaling. One of the unique features of Eph/ephrin signaling is the fact that both receptors and ligands are competent to transduce a signaling cascade upon interaction. Eph-activated signaling is termed forward, and ephrin-activated signaling is termed reverse. Another level of complexity stems from the fact that interactions between Eph receptors and ephrins can happen in trans (between two opposing cells) or in cis (within the same cell). It is commonly assumed that trans interactions are activating while cis interactions are inhibiting.3 Eph-Ephrin signaling functions in a variety biological processes including diverse assegmentation of the somites and rhombomeres, the formation of blood vessels, Axon guidance and fasciculation, migration of the neural crest and metastasis of transformed cells etc.
EphB6 is an unusual Eph receptor, lacking catalytic capacity due to alterations in its kinase domain. Interestingly, increased metastatic activity is associated with reduced EphB6 receptor expression in several tumor types, including breast cancer. This emphasizes the potential of EphB6 to act as a suppressor of cancer aggressiveness. Unusual EphB6 effect on cancer cells matches its unique signaling properties because its phosphorylation is provided by EphB1, EphB4 or a Src family kinase etc. It was shown that restoration of EphB6 expression in invasive breast cancer cells supports actin-dependent spreading and attachment and blocks invasiveness. EphB6 stimulation induces its tyrosine phosphorylation, which is crucial for its function and is mediated by the EphB4 receptor. This is accompanied by EphB6–c-Cbl interaction and phosphorylation of c-Cbl partner, the Abl kinase. Cbl silencing suppresses Abl phosphorylation, cell adhesion, and morphologic changes and blocks the ability of EphB6 to inhibit invasiveness, confirming its importance for EphB6 activity.4 In addition to affecting invasiveness phenotype, EphB6 overexpression was also responsible for altering the growth rate and colony-forming efficiency of MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 cells in a cell-line-specific manner. Thus, EphB6 may represent a useful prognostic marker and a promising target for therapeutic approaches.5
EphB6 is an unusual Eph receptor, lacking catalytic capacity due to alterations in its kinase domain. Interestingly, increased metastatic activity is associated with reduced EphB6 receptor expression in several tumor types, including breast cancer. This emphasizes the potential of EphB6 to act as a suppressor of cancer aggressiveness. Unusual EphB6 effect on cancer cells matches its unique signaling properties because its phosphorylation is provided by EphB1, EphB4 or a Src family kinase etc. It was shown that restoration of EphB6 expression in invasive breast cancer cells supports actin-dependent spreading and attachment and blocks invasiveness. EphB6 stimulation induces its tyrosine phosphorylation, which is crucial for its function and is mediated by the EphB4 receptor. This is accompanied by EphB6–c-Cbl interaction and phosphorylation of c-Cbl partner, the Abl kinase. Cbl silencing suppresses Abl phosphorylation, cell adhesion, and morphologic changes and blocks the ability of EphB6 to inhibit invasiveness, confirming its importance for EphB6 activity.4 In addition to affecting invasiveness phenotype, EphB6 overexpression was also responsible for altering the growth rate and colony-forming efficiency of MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 cells in a cell-line-specific manner. Thus, EphB6 may represent a useful prognostic marker and a promising target for therapeutic approaches.5
REFERENCES
1. Brantley-Sieders, D.M. & Chen, J.: Angiogenesis. 7:17, 2004
2. Murai, K.K. & Pasquale, E.B.: J. Cell Sci. 116:2823, 2003
3. Arvanitis, D. & Davy, A.: Genes & Dev. 22:416, 2008
4. Truitt, L. et al: Cancer Res. 70: 1141–53, 2010
5. Fox, B.P. & Kandpal, P.R. : Oncogene 28:1706-13, 2009
2. Murai, K.K. & Pasquale, E.B.: J. Cell Sci. 116:2823, 2003
3. Arvanitis, D. & Davy, A.: Genes & Dev. 22:416, 2008
4. Truitt, L. et al: Cancer Res. 70: 1141–53, 2010
5. Fox, B.P. & Kandpal, P.R. : Oncogene 28:1706-13, 2009
Products are for research use only. They are not intended for human, animal, or diagnostic applications.
Параметры
Cat.No.: | CP10306 |
Antigen: | Raised against recombinant human EphB6 fragments expressed in E. coli. |
Isotype: | Mouse IgG1 |
Species & predicted species cross- reactivity ( ): | Human, Mouse, Rat |
Applications & Suggested starting dilutions:* | WB 1:1000 IP n/d IHC 1:50 - 1:200 ICC n/d FACS n/d |
Predicted Molecular Weight of protein: | 110 kDa |
Specificity/Sensitivity: | Detects endogenous EphB6 proteins without cross-reactivity with other family members. |
Storage: | Store at -20°C, 4°C for frequent use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
*Optimal working dilutions must be determined by end user.
Документы
Информация представлена исключительно в ознакомительных целях и ни при каких условиях не является публичной офертой