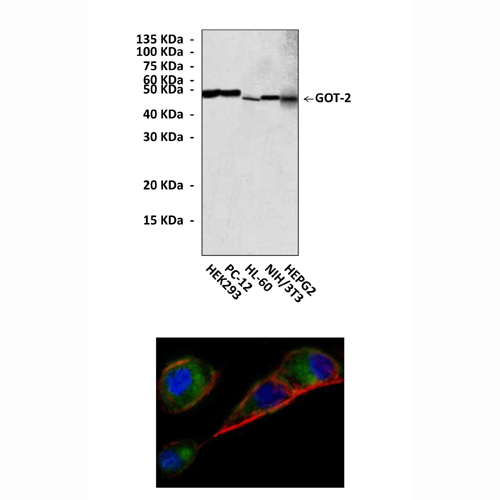
Anti-GOT-2: Mouse Glutamic-Oxaloacetic Transaminase 2 Monoclonal Antibody |
 |
BACKGROUND Glutamic-oxaloacetic transaminase is a pyridoxal phosphate-dependent enzyme which exists in cytoplasmic and inner-membrane mitochondrial forms, GOT1 and GOT2, respectively. GOT plays a role in amino acid metabolism and the urea and tricarboxylic acid cycles. The two enzymes are homodimeric and show close homology. GOT2 is important for metabolite exchange between mitochondria and cytosol. It facilitates cellular uptake of long-chain free fatty acids.1
GOT is normally present in liver and heart cells. Serum GOT (SGOT) is released into blood when the liver or heart is damaged. The blood SGOT levels are thus elevated with liver damage (for example, from viral hepatitis) or with an insult to the heart (for example, from a heart attack). Some medications can also raise SGOT levels. SGOT is also called aspartate aminotransferase (AST).2
REFERENCES
1. Morino, Y. et al: Biochem. and Biophys. Res Communs. 13: 348-53, 1963
2. Gaze, D.C.: Curr. Opin. Invest. Drugs 8:711–717, 2007
2. Gaze, D.C.: Curr. Opin. Invest. Drugs 8:711–717, 2007
Products are for research use only. They are not intended for human, animal, or diagnostic applications.
Параметры
Cat.No.: | CP10117 |
Antigen: | Purified recombinant human GOT-2 fragment expressed in E. coli. |
Isotype: | Mouse IgG |
Species & predicted species cross- reactivity ( ): | Human, Mouse, Rat |
Applications & Suggested starting dilutions:* | WB 1:1000 IP n/d IHC n/d ICC 1:200 FACS n/d |
Predicted Molecular Weight of protein: | 47 kDa |
Specificity/Sensitivity: | Detects endogenous GOT-2 proteins without cross-reactivity with other related proteins. |
Storage: | Store at -20°C, 4°C for frequent use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
*Optimal working dilutions must be determined by end user.
Документы
Информация представлена исключительно в ознакомительных целях и ни при каких условиях не является публичной офертой