Anti-Noggin: Monoclonal Noggin Antibody |
 |
BACKGROUND The gene noggin, originally cloned in Xenopus, encodes a secreted factor expressed in the Spemann organizer, where it functions to oppose the ventralizing influence of bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs). Noggin protein acts by binding directly to BMPs, thereby preventing them from interacting with their receptors. The interaction between BMPs and Noggin, is critical for normal development.1 Recently, it was shown that Noggin and bFGF cooperate to maintain the pluripotency of human embryonic stem cells in the absence of feeder layers. This feeder-free culture system will provide a more reliable alternative for future therapeutic applications of hES cells.2
REFERENCES
1. MacMahon, J. A. et al., Gene Dev 12:1438, 1998.
2. Wang, G. et al., Biochem Biophys Res Commun 330:934, 2005.
2. Wang, G. et al., Biochem Biophys Res Commun 330:934, 2005.
Products are for research use only. They are not intended for human, animal, or diagnostic applications.
Параметры
Cat.No.: | CB10536 |
Antigen: | Recombinant human Noggin protein |
Isotype: | Mouse Monoclonal IgG1 |
Species & predicted species cross- reactivity ( ): | Human |
Applications & Suggested starting dilutions:* | WB 1:1000 IP n/d IHC n/d ICC n/d FACS n/d |
Predicted Molecular Weight of protein: | 27 kDa |
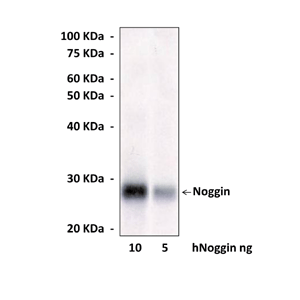
Specificity/Sensitivity: | Reacts specifically with human Noggin in Western Blot applications. |
Storage: | -20° |
*Optimal working dilutions must be determined by end user.
Документы
Информация представлена исключительно в ознакомительных целях и ни при каких условиях не является публичной офертой