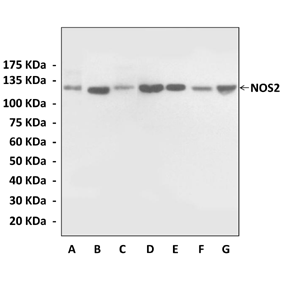
Anti-NOS2: Rabbit NOS2 Antibody |
 |
BACKGROUND Nitric oxide synthases (NOSs) comprise a family of enzymes that generate the freely diffusible, free radical gas NO, by the conversion of L-arginine to L-citrulline in the presence of O2 and NADPH. Bioactive derivatives of NO (NOx) are produced depending on the redox state of the cell and the availability of substrates and cofactors. The three NOSs arise from separate genes, but each NOS molecule is composed of a calmodulin binding domain that links a carboxyl terminal flavin-containing reductase domain with an amino terminal heme-containing oxygenase domain. Neuronal NOS (nNOS or NOS1) and endothelial NOS (eNOS or NOS3) are constitutively active isoforms with calmodulin binding (and, consequently, enzyme activity) regulated by physiological [Ca2+]. Although inducible NOS (iNOS or NOS2) binds calmodulin tightly, it is independent of intracellular calcium levels.1
Inducible NOS2/iNOS is an inflammation-responsive enzyme that is upregulated in acute and chronic inflammation as part of host defense and the wound-healing process. Upregulation of this enzyme leads to increased NO production, by which it affects the redox state of cells. Aberrant expression of NOS2/iNOS has been observed in many types of solid tumors, including breast and colon cancer, and also in melanoma. NO can both cause DNA damage and protect from cytotoxicity and either inhibit or stimulate cell proliferation and migration as well as apoptosis.2 The effect of NO will be dependent on the microenvironment, including tissue oxygen tension and local superoxide concentrations. Additionally, it was shown that NOS2/iNOS expression correlates with increased Akt phosphorylation in breast tumors and that NO induces Akt phosphorylation and activation of the oncogenic Akt pathway in breast cancer cells in culture. There is a relationship between NOS2/iNOS expression, increased NO production, and the induction of a basal-like transcription pattern and poor prognosis in ER-negative breast tumors.3
Inducible NOS2/iNOS is an inflammation-responsive enzyme that is upregulated in acute and chronic inflammation as part of host defense and the wound-healing process. Upregulation of this enzyme leads to increased NO production, by which it affects the redox state of cells. Aberrant expression of NOS2/iNOS has been observed in many types of solid tumors, including breast and colon cancer, and also in melanoma. NO can both cause DNA damage and protect from cytotoxicity and either inhibit or stimulate cell proliferation and migration as well as apoptosis.2 The effect of NO will be dependent on the microenvironment, including tissue oxygen tension and local superoxide concentrations. Additionally, it was shown that NOS2/iNOS expression correlates with increased Akt phosphorylation in breast tumors and that NO induces Akt phosphorylation and activation of the oncogenic Akt pathway in breast cancer cells in culture. There is a relationship between NOS2/iNOS expression, increased NO production, and the induction of a basal-like transcription pattern and poor prognosis in ER-negative breast tumors.3
REFERENCES
1. Hoit, B.D.: Circul. Res. 89:289-91, 2001
2. Weinberg, J.B.: Mol. Med. 4:557-91, 1998
3. Glynn, S.A. et al: J. Clin. Invest. 120:3843-54, 2010
2. Weinberg, J.B.: Mol. Med. 4:557-91, 1998
3. Glynn, S.A. et al: J. Clin. Invest. 120:3843-54, 2010
Products are for research use only. They are not intended for human, animal, or diagnostic applications.
Параметры
Cat.No.: | CA1330 |
Antigen: | Short peptide from human NOS2 sequence. |
Isotype: | Rabbit IgG |
Species & predicted species cross- reactivity ( ): | Human, Mouse, Rat |
Applications & Suggested starting dilutions:* | WB 1:1000 IP n/d IHC 1:50 - 1:200 ICC n/d FACS n/d |
Predicted Molecular Weight of protein: | 130 kDa |
Specificity/Sensitivity: | Detects endogenous levels of NOS2 proteins without cross-reactivity with other related proteins. |
Storage: | Store at -20°C, 4°C for frequent use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
*Optimal working dilutions must be determined by end user.
Документы
Информация представлена исключительно в ознакомительных целях и ни при каких условиях не является публичной офертой