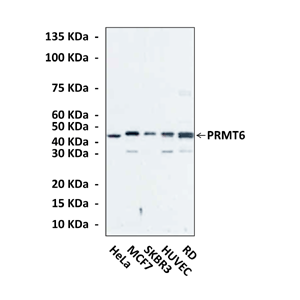
Anti-PRMT6: Monoclonal Protein Arginine N-Methyltransferase 6 Antibody |
 |
BACKGROUND The family of protein arginine N-methyltransferases (PRMTs) catalyze the sequential transfer of a methyl group from AdoMet to the side chain nitrogens of arginine residues within proteins to form methylated arginine derivatives and S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine.1 There are eleven different PRMT genes (PRMT1-11) whose biological function remains under explored. With regard to the dimethylation product, PRMTs are distinguished into type I enzymes, which catalyze the asymmetric NG,NG-dimethyl-arginine, and the type II subfamily, which consists of PRMT5, PRMT7, and PRMT9 and generates symmetric NG,NG′-dimethylation. PRMT2 was isolated based on its sequence similarity with PRMT1. So far no methyltransferase activity has been revealed for PRMT2.2 PRMTs regulate various cellular processes such as DNA repair and transcription, RNA processing, signal transduction, and nucleo-cytoplasmic localization. Like histone lysine methylation, methylation of histone arginine residues can either induce or inhibit transcription depending on the residue being modified and the type of methylation being introduced.3
REFERENCES
1. Litt M et al.: Biosci Rep. 29:131-41, 2009.
2. Meyer R et al.: J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 107:1-14, 2007.
3. Lee YH. & Stallcup MR: Mol Endocrinol. 23:425-33, 2009.
2. Meyer R et al.: J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 107:1-14, 2007.
3. Lee YH. & Stallcup MR: Mol Endocrinol. 23:425-33, 2009.
Products are for research use only. They are not intended for human, animal, or diagnostic applications.
Параметры
Cat.No.: | CC10009 |
Antigen: | An E. coli-expressed purified recombinant fragment of human PRMT6 (aa120-280) |
Isotype: | Mouse monoclonal IgG2b |
Species & predicted species cross- reactivity ( ): | Human, Rat, Mouse |
Applications & Suggested starting dilutions: | WB 1:1000 IP 1:50 IHC n/d ICC n/d FACS n/d |
Predicted Molecular Weight of protein: | 45 kDa |
Specificity/Sensitivity: | Detects endogenous levels of PRMT6 proteins in various cell lysates. |
Storage: | Store at -20°C, 4°C for frequent use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
*Optimal working dilutions must be determined by end user.
Документы
Информация представлена исключительно в ознакомительных целях и ни при каких условиях не является публичной офертой