Anti-SRC-3/AIB-1: Monoclonal Steroid Receptor Coactivator-3 Antibody |
 |
BACKGROUND Nuclear hormone receptors are ligand-dependent transcription factors that require coactivators to regulate target gene expression. The steroid receptor coactivator-3 (SRC-3), also known as p/CIP, RAC3, AIB1, ACTR and TRAM-1, is a cancer-amplified coactivator in the SRC gene family that also contains SRC-1 and SRC-2. SRC-3 interacts with nuclear receptors and certain other transcription factors, recruits histone acetyltransferases and methyltransferases for chromatin remodeling and facilitates target gene transcription.1 SRC-3 phosphorylation and methylation have been shown to regulate such coactivator complex assembly.2,3 Accumulated results from both ex vivo and animal model studies indicate that SRC-3 plays important roles in many biological processes involving cell proliferation, cell migration, cell differentiation, somatic growth, sexual maturation, female reproductive function, and vasoprotection1. Moreover, SRC-3 has been associated with multiple cancers, including breast, gastric and prostate cancers.4
REFERENCES
1. Liao L et al.: J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 83:3, 2002.
2. Feng Q et al.: Mol Cell Biol 26:7846, 2006.
3. Wu H et al.: J Biol Chem 281:21848, 2006.
4. Yan J et al.: Acta Pharmacol Sin 27:387, 2006.
2. Feng Q et al.: Mol Cell Biol 26:7846, 2006.
3. Wu H et al.: J Biol Chem 281:21848, 2006.
4. Yan J et al.: Acta Pharmacol Sin 27:387, 2006.
Products are for research use only. They are not intended for human, animal, or diagnostic applications.
Параметры
Cat.No.: | CB10247 |
Antigen: | Recombinant human SRC-3/ AIB-1 protein N-terminal fragments (1-250 aa) |
Isotype: | Mouse Monoclonal IgG1 |
Species & predicted species cross- reactivity ( ): | Human |
Applications & Suggested starting dilutions: | WB 1:1000 IP n/d IHC (Paraffin) n/d ICC n/d FACS n/d |
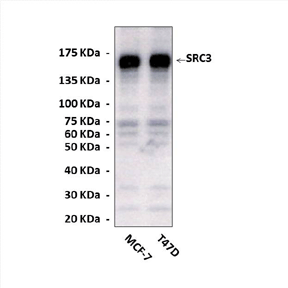
Predicted Molecular Weight of protein: | 160 kDa |
Specificity/Sensitivity: | Detects endogenous phospho-human and mouse SRC-3/AIB-1. |
Storage: | Store at 4° for frequent use; at -20° for at least one year. |
*Optimal working dilutions must be determined by end user.
Документы
Информация представлена исключительно в ознакомительных целях и ни при каких условиях не является публичной офертой