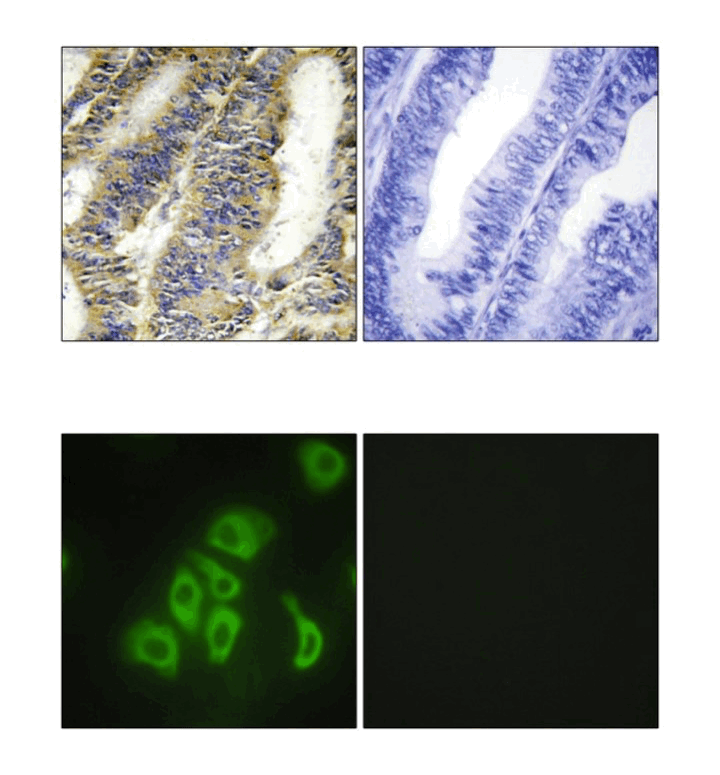
Anti-TNF-α: Rabbit Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha Antibody |
 |
BACKGROUND Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) is a pleiotropic inflammatory cytokine. It is a trimeric protein encoded within the major histocompatibility complex. It was first identified in its 17 kD secreted form, but further research then showed that a noncleaved 27kd precursor also existed in a transmembrane form. This cytokine serves a variety of functions. It possesses both growth stimulating properties and growth inhibitory processes, and it appears to have self- regulatory properties as well.
TNF-alpha is produced by several types of cells, in particular by macrophages.1 It has been suggested that the two beneficial functions of TNF-alpha may lead to its continued expression. Firstly, low levels of the cytokine may aid in maintaining homeostasis by regulating the body's circadian rhythm. Furthermore, low levels of TNF-alpha promote the remodeling or replacement of injured and senescent tissue by stimulating fibroblast growth. Additional beneficial functions of TNF-alpha include its role in the immune response to bacterial, and certain fungal, viral, and parasitic invasions, as well as its role in the necrosis of specific tumors. Lastly TNF-alpha acts as a key mediator in the local inflammatory immune response.
The pathological activities of TNF-alpha have attracted much attention. For instance, although TNF-alpha causes necrosis of some types of tumors, it promotes the growth of other types of tumor cells. High levels of TNF-alpha correlate with increased risk of mortality. TNF-alpha participates in both inflammatory disorders of inflammatory and non-inflammatory origin. Originally sepsis was believed to result directly from the invading bacteria itself, but it was later recognized that host system proteins, such as TNF-alpha, induced sepsis in response.2,3
TNF-alpha shares only 36% amino acid sequence homology with TNF-alpha, also called lymphotoxin (LT). Yet, the tertiary structures of the two proteins are remarkably similar, and both bind to TNF receptors. TNF signals through 2 separate receptors - TNFRSF1A and TNFRSF1B, both members of the TNF receptor superfamily. Activation by the homotrimeric ligand results in receptor trimerization. TNFRSF1A trimers result in the activation of NF-kB through MAPK and caspase pathways, leading to apoptosis. In contrast, a heterocomplex of both TNFRSF1A and TNFRSF1B recruits proteins such as BIRC2 and BIRC3, which are apoptotic inhibitors. As both TNF-alpha and IL-1 stimulate the MAPK signaling module and activate NFkB, they are synergistic and complement each other's activity.4
REFERENCES
1. Old LJ et al.: Science, 230:630–2, 1985.
2. Pennica D et al.: Nature, 312: 724–9, 1984.
3. Locksley RM et al.: Cell, 104: 487–501, 2001.
4. Wajant H et al.: Cell Death Differ. 10: 45–65, 2003.
2. Pennica D et al.: Nature, 312: 724–9, 1984.
3. Locksley RM et al.: Cell, 104: 487–501, 2001.
4. Wajant H et al.: Cell Death Differ. 10: 45–65, 2003.
Products are for research use only. They are not intended for human, animal, or diagnostic applications.
Параметры
Cat.No.: | CG1601 |
Antigen: | recombinant human TNF-alpha |
Isotype: | Rabbit IgG |
Species & predicted species cross- reactivity ( ): | Human, Mouse, Rat |
Applications & Suggested starting dilutions:* | WB 1:1000 IP 1:50 IHC n/d ICC n/d FACS n/d |
Predicted Molecular Weight of protein: | 25 kDa |
Specificity/Sensitivity: | Detects endogenous levels of TNF-alpha proteins in normal cell lysates. |
Storage: | Store at -20°C, 4°C for frequent use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
*Optimal working dilutions must be determined by end user.
Документы
Информация представлена исключительно в ознакомительных целях и ни при каких условиях не является публичной офертой