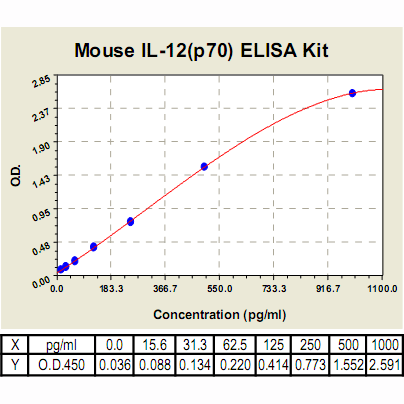
IL-12 (p70) ELISA Kit, Mouse |
 |
BACKGROUND Interleukin-12 (IL-12p70) is a heterodimeric cytokine that has a molecular weight of 75 kDa and is composed of disulfide-bounded two subunits: IL-12p35 and IL-12p40. It is part of a large family of cytokines that also comprises IL-23 and IL-27, is produced mostly by phagocytic cells in response to bacteria, bacterial products, and intracellular parasites, and to some degree by B lymphocytes. Further studies revealed that IL-12 was a major actor, if not the key trigger (the signature cytokine), of Th1 maturation in Th precursor cells. It induces the production of large amounts of IFN-gamma, which is itself considered to be the Th1-effector signature molecule. Cellular, or Th1, immunity has been suggested to play a crucial role in defenses against intracellular microorganisms, including all viruses and a number of bacteria, parasites and fungi. This view was largely supported by studies of experimental infections in knockout mice lacking IL-12 or IL-12 receptor. In vivo IL-12 acts primarily at three stages during the innate resistance/adaptive immune response to infection: 1. Early in the infection, IL-12 is produced and induces production from NK and T cells of IFN-gamma , which contributes to phagocytic cell activation and inflammation; 2. IL-12 and IL-12- induced IFN-gamma favor Thl cell differentiation by priming CD4+ T cells for high IFN-gamma production; and 3. IL-12 contributes to optimal IFN-gamma production and to proliferation of differentiated Th l cells in response to antigen. The early preference expressed in the immune response depends on the balance between IL-12, which favors Thl responses, and IL-4, which favors Th2 responses. Thus IL-12 represents a functional bridge between the early nonspecific innate resistance and the subsequent antigen-specific adaptive immunity.1 Furthermore, it has also been found that direct interaction of B cells with IL-12 leads to cell proliferation and differentiation, IFN-gamma production and production of the type 2 cytokine IL-4.2 In addition, it was also shown that IL-12 modulates a number of genes involved in leukocyte trafficking. Thus, IL-12 is not only an important proinflammatory cytokine, which induces production of IFN-gamma and subsequent activation of phagocytic cells but also plays a major role in regulating the migration and proper positioning of effector cells.3
IL-12 signaling was mediated by a heterodimeric receptor — IL-12Rbeta1 and IL-12Rbeta2 — which is expressed by NK and T cells. IL-12p70 (IL-12) binds to the IL-12 receptor complex, resulting in the rapid phosphorylation of tyrosine residues on STAT4, a transcription factor that is exclusively present in the cells of the immune system. Stat4 mediates the downstream IL-12 signaling and interferon (IFN)-gamma production.4
IL-12 signaling was mediated by a heterodimeric receptor — IL-12Rbeta1 and IL-12Rbeta2 — which is expressed by NK and T cells. IL-12p70 (IL-12) binds to the IL-12 receptor complex, resulting in the rapid phosphorylation of tyrosine residues on STAT4, a transcription factor that is exclusively present in the cells of the immune system. Stat4 mediates the downstream IL-12 signaling and interferon (IFN)-gamma production.4
REFERENCES
1. Watford, W.T. et al: Cytokine Growth factor Rev. 14:361-8, 2003
2. Skok, J. et al: J. Immunol. 163:5257-64, 1999
3. Sinigaglia, F. et al: Immunol. Rev. 170:65-72, 1999
4. Karpuzoglu, E. et al: Endocrinol. 150:1310-20, 2009
2. Skok, J. et al: J. Immunol. 163:5257-64, 1999
3. Sinigaglia, F. et al: Immunol. Rev. 170:65-72, 1999
4. Karpuzoglu, E. et al: Endocrinol. 150:1310-20, 2009
Products are for research use only. They are not intended for human, animal, or diagnostic applications.
Параметры
Cat.No.: | CL0422 |
Target Protein Species: | Mouse |
Range: | 15.6 pg/ml – 1000pg/ml |
Specificity: | No detectable cross-reactivity with any other cytokines |
Storage: | Store at 4°C. Use within 6 months. |
ELISA Kits are based on standard sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay technology. Freshly prepared standards, samples, and solutions are recommended for best results.
Документы
Информация представлена исключительно в ознакомительных целях и ни при каких условиях не является публичной офертой