Anti-GABPA: Monoclonal GA-Binding Protein Transcription Factor Antibody |
 |
BACKGROUND The GA-binding protein transcription factor, also called nuclear respiratory factor-2 (NRF2), was originally identified by its role in the expression of the adenovirus E4 gene. GA-binding protein alpha chain (GABPA) is one of three GA-binding protein transcription factor subunits, which functions as a DNA-binding subunit.1 The GABP complex contributes to the transcriptional regulation of a number of subunits of mitochondrial enzymes, including cytochrome c oxidase and mitochondrial transcription factor A.2 Because of its chromosomal localization and ability to form heterodimers with other polypeptides, this gene may play a role in the Down Syndrome phenotype.3
REFERENCES
1. Watanabe H et al.: Mol. Cell. Biol. 13: 1385-1391, 1993.
2. Guo A et al.: J. Comp. Neurol. 417: 221-232, 2000.
3. Chrast R et al.: Genomics 28:119-122, 1995.
2. Guo A et al.: J. Comp. Neurol. 417: 221-232, 2000.
3. Chrast R et al.: Genomics 28:119-122, 1995.
Products are for research use only. They are not intended for human, animal, or diagnostic applications.
Параметры
Cat.No.: | CC10006 |
Antigen: | An E. coli-expressed recombinant protein containing human GABPA (aa120-190) sequence. |
Isotype: | Mouse Monoclonal IgG1 |
Species & predicted species cross- reactivity ( ): | Human, Mouse |
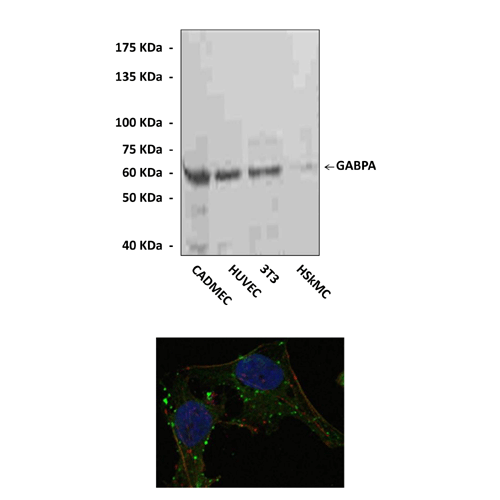
Applications & Suggested starting dilutions: | WB 1:1000 IP n/d IHC n/d ICC 1:200 - 1:1000 FACS n/d |
Predicted Molecular Weight of protein: | 60 kDa |
Specificity/Sensitivity: | This monoclonal antibody detects endogenous levels of GABPA proteins in various cell lysates. |
Storage: | Store at -20°C, 4°C for frequent use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
*Optimal working dilutions must be determined by end user.
Документы
Информация представлена исключительно в ознакомительных целях и ни при каких условиях не является публичной офертой